Integration Overview
Version support: 4.2.1-7.1.3
The Avaya TSAPI integration allows NICE Uptivity to receive call-related events and metadata from AES. This integration must be paired with an audio capture method to provide an audio source for recordings. NICE Uptivity supports the following audio capture methods in conjunction with TSAPI:
- Passive VoIP
- DMCC (using either SSC, SO, or MR)
- TDM (using Ai-Logix audio capture cards)
- SSC and SO over active T1 trunks
- SIPREC/ACME Packet SBC
Need-to-Knows
For information and procedures related to configuration, consult the Uptivity installation team.
NICE Uptivity only uses Avaya TSAPI to receive CTI events and metadata. Therefore, TSAPI integration must be paired with a separate audio capture source. In addition, Avaya TSAPI is used as part of a number of other integrations, such as those using service observe or single step conferencing. You may need to refer to other customer guides for audio capture methods or integrations for additional limitations, licensing requirements, and customer integration and administration tasks.
Terminology
To ensure a common frame of reference, this guide uses the following terms in conjunction with this Avaya integration:
|
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
| AACC | Avaya Aura Contact Center. The AACC server hosts software that provides agent-related CTI events. |
| AES | Application Enablement Services. The AES server hosts software that provides phone-related CTI events. |
| Avaya CMS | Avaya Call Management System. This contact center product is designed for businesses with complex contact center operations and high call volume. Sometimes referred to as Avaya CM. |
| DMCC | Device Media Call Control. This functionality of the Avaya AES server provides a means of active recording via VoIP, even for endpoints that are not IP telephones. |
| GEDI | Graphically-Enhanced DEFINITY Interface. Used by the customer or Avaya vendor to configure the Avaya CMS. |
| MR | Multiple Registration. Avaya functionality that allows the customer to register up to three devices against a single softphone extension. |
| SO | Service Observe. Avaya functionality that allows a person or device to listen to a call in progress. |
| SSC | Single Step Conference. Avaya functionality that can be used to establish a conference between a recording device, the agent's phone and a corresponding softphone on the AES server. |
| TDM | Formally, Time Division Multiplexing. In the context of this guide, traditional telephony using analog or digital lines (as opposed to VoIP). |
| TSAPI | Telephone Services Application Programming Interface. Avaya TSAPI is the actual software that provides the call control events and metadata to NICE Uptivity. |
| S8300, S8500, S8700 | These are common models of Avaya PBX equipment. |
Known Limitations
NICE Uptivity does not support using bridged appearances in an Avaya TSAPI-based recording environment due to the way TSAPI handles call notification events for bridged calls. Avaya sends established messages on all CTI monitors which have bridged appearances. Consider this example:
- Stations A, B, and C all have Bridge Appearance 1 programmed.
- A call is delivered to Appearance 1.
- The call rings to Stations A, B, and C on the bridged line.
- Station A answers the call on Bridged Appearance .1
- The call begins recording when Station A answers the call.
If Station A remains active for the entire duration of the call, the entire call is recorded. If Station B joins the call and Station A remains in the call, the entire call is recorded. However, if Station A leaves the bridge, recording ends. Further, recording will not resume even if Station A later returns to the bridge and if additional recorded parties enter the established bridge, they will not be recorded.
This limitation applies to any recording integration that uses TSAPI for CTI, and is in addition to limitations specific to the audio acquisition method.
Avaya Requirements
If you are using Avaya TSAPI in conjunction with another integration, refer to that integration’s customer guide as well for additional software and licensing requirements.
Hardware
- Avaya S8300, S8500, or S8700 PBX
Software
- Avaya CM v3.1 through 7.0
- Avaya AES with SP 4 or later through 7.0.1
- Avaya TSAPI (or CVCT) Client
|
32-bit |
64-bit |
AES/TSAPI |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 2008 R2 | X |

|
5.2 or higher |
| Windows 2012 R2 | X |

|
6.3.3 or higher |
| Windows 2016 | X |

|
7.1 or higher |
Licensing
- One (1) TSAPI Basic license for each device or group that will be monitored for events.
- For TSAPI as part of a DMCC-SSC or DT-SSC integration:
- One (1) additional TSAPI basic license per concurrent recording channel.
- One (1) additional TSAPI basic license for the recording skill. In most implementations, a skill is created for recording and all agents to be recorded are assigned that skill.
For example, a DMCC-SSC integration recording 800 agents on 600 recording channels would require a total of 1401 TSAPI licenses.
Uptivity Requirements
NICE Uptivity requirements are outlined in the section for your specific audio capture method.
Passive Recording Examples
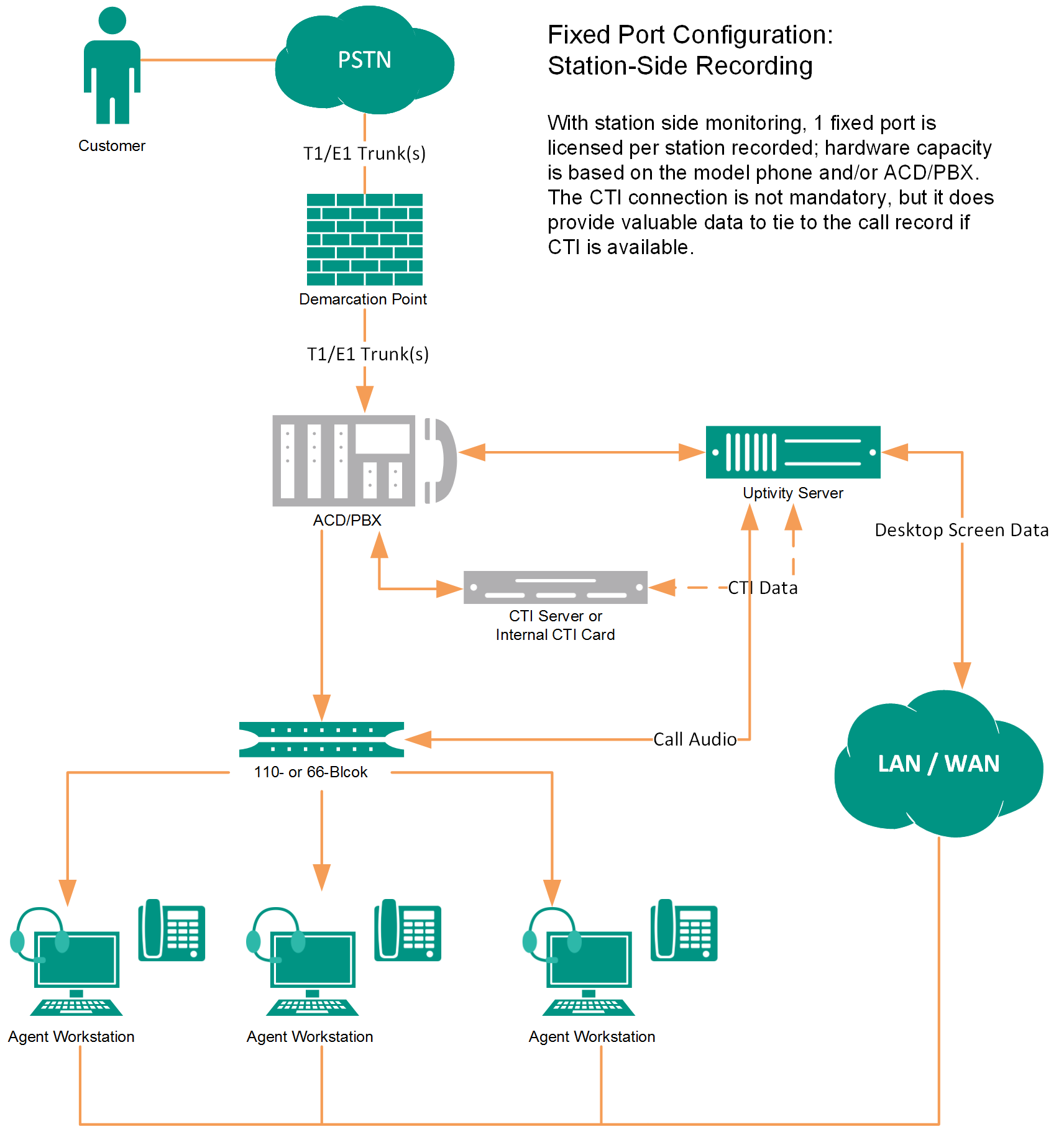
TDM Station-Side
In station-side recording, NICE Uptivity acquires audio from the agent station side of the conversation. Physical audio capture cards installed in the NICE Uptivity recording server have a wired connection to each recorded phone. A CTI connection using TSAPI can provide tighter call control and additional metadata for each call.
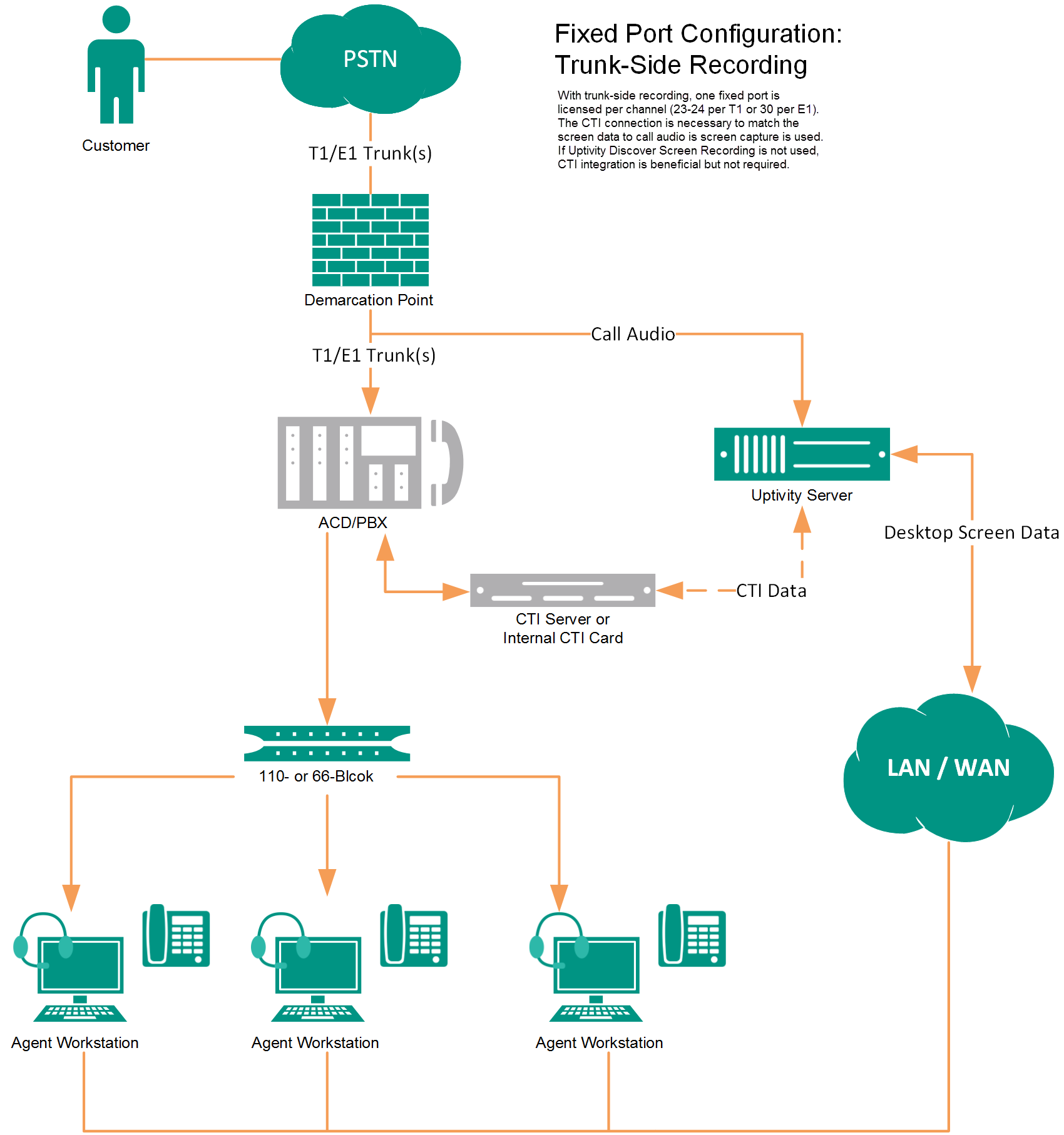
TDM Trunk-Side
In trunk-side recording, physical audio capture cards installed in the NICE Uptivity recording server have a wired connection to each T1/E1 trunk to be recorded, and record from the trunk side of the conversation. A CTI connection using TSAPI can provide events on which to base recording decisions as well as additional metadata for each call.
Active Recording Examples
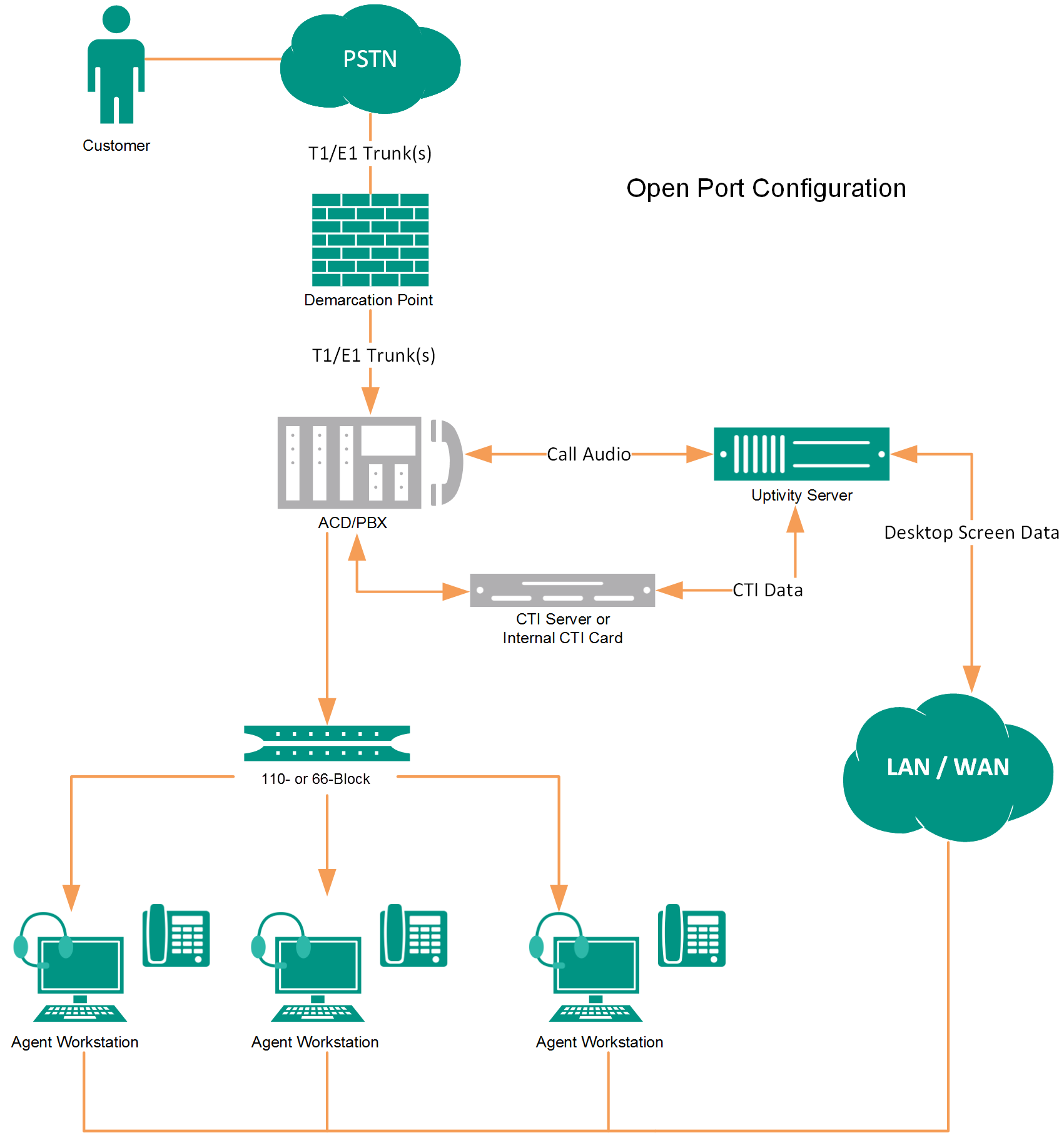
Service Observe (SO) / SSC Trunk Recording (TDM)
In Open Port/Service Observe recording, NICE Uptivity uses the Avaya Service Observe or Single Step Conference feature to record. Audio capture cards in the recording server are connected to the Avaya PBX through a T1/E1 tie line or through direct analog lines. With appropriate ACD/PBX permissions, these ports can record any device in the system. Since these channels have dial tone at the PBX level, they can also be used to play audio back to specified devices.
This method has some limitations. The preferred method for recording open ports is single step conferencing. A CTI connection using TSAPI provides events to trigger recording and call control, as well as additional metadata for each call.
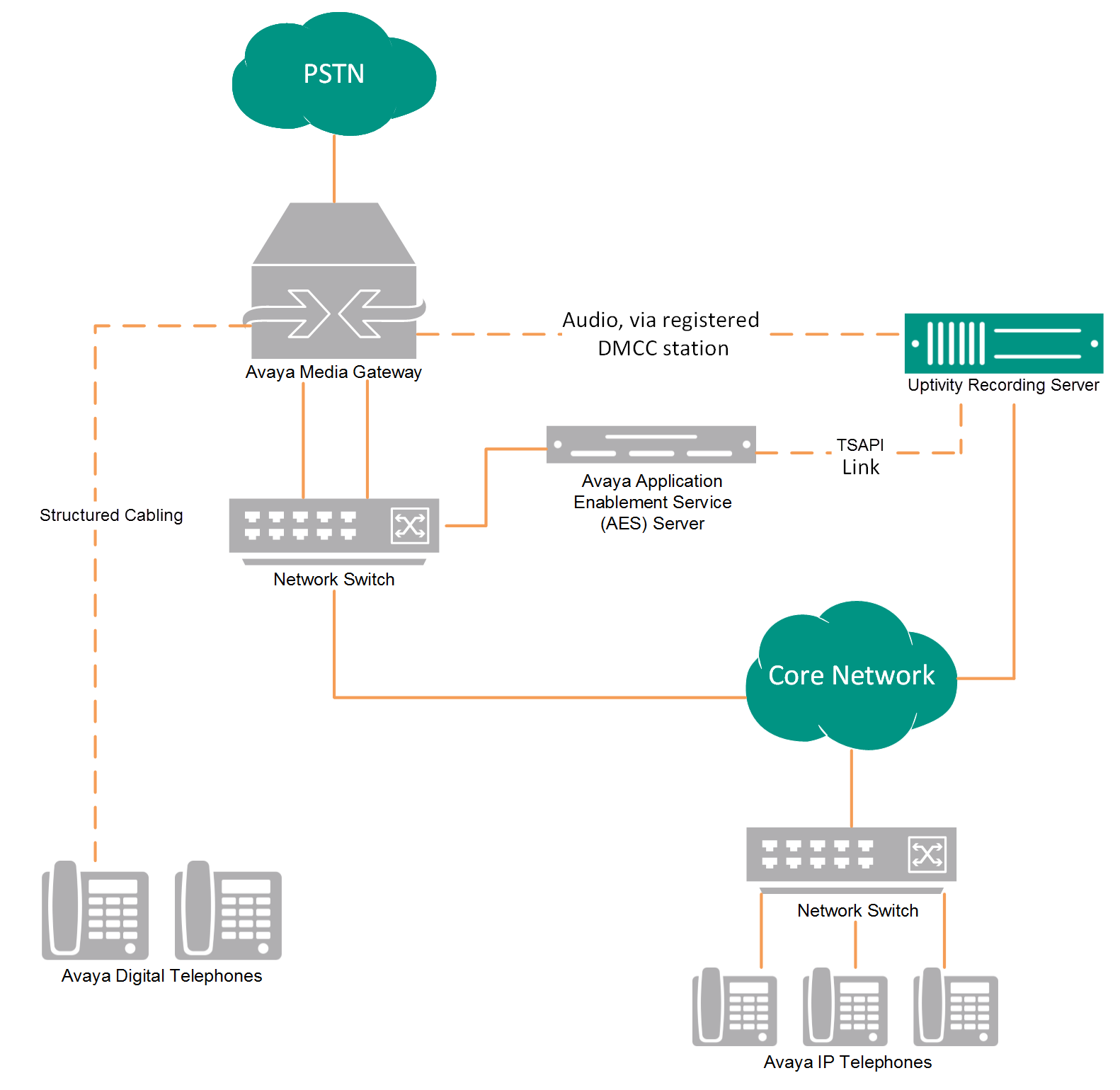
Service Observe / SSC DMCC Recording (VoIP)
DMCC recording uses media redirection from Avaya to record calls without the use of physical connections to the NICE Uptivity recording server (other than standard network connections). NICE Uptivity supports DMCC using Service Observe (SO), single step conference (SSC), and multiple registration (MR). TSAPI is used in all DMCC recording integrations for call control, messaging, and metadata.
Customer Configuration Overview
The following list provides a high-level overview of the customer configuration steps in Avaya TSAPI integrations. Click "Next Section" at the bottom of the page for instructions on each step.
- Complete all necessary physical and IP connections between the recording server(s) and the LAN.
- Obtain any necessary Avaya software and licensing.
- Configure the CTI Link on the Avaya CM.
- Create the CTI User Account on the AES Server.
- Verify the TSAPI Link on the AES Server.
- Verify TSAPI License Availability.
- If you want to, Configure UCID.
- Complete the tasks and procedures detailed in the section specific for your audio acquisition method.
|
|
|